Podocyte (CL_0000653)
Podocyte is a cell type in renal corpuscle and wraps around the capillary of the glomerulus in the kidney. Renal corpuscle filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins and filtering out smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars in the formation of urine. Podocytes are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the Bowman's capsule.
Above is a graphic of podocyte on the outer surfaces of a section of glomerular capillary. Cell body, primary processes, and pedicles are shown. Neighboring cells with interdigitating pedicles not shown. Copyright: Melissa Clarkson.
Cell Ontology (CL) ID: CL_0000653
CL definition: A glomerular visceral epithelial cell is a specialized kidney epithelial cell that contains "feet" that interdigitate with the "feet" of other glomerular epithelial cells. [database_cross_reference: GOC:tfm]
Synonyms: glomerular visceral epithelial cell; epithelial cell of visceral layer of glomerular capsule; glomerular podocyte
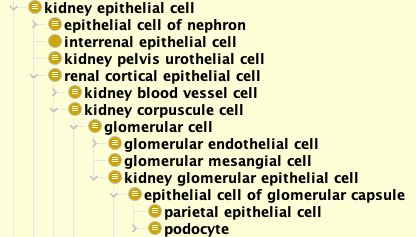
Cell Hierarchy (defined by CL):
Podocyte hierarchy according to the Cell Ontology (CL):
Above is a graphic (prepared by: Alex Diehl) of CL hierarchy of podocyte and its associated cell types represented in the CL. Later on we will show a cell hierarchy with live links to other cell types.
Location (defined by CL and UBERON):
Podocyte wraps around the capillary of the glomerulus in the kidney.
'part of' some 'visceral layer of glomerular capsule' (UBERON_0005751)
Connections and Vicinity:
Podocytes are neighbors of many other cell types such as afferent and efferent arteriole endothelial cells, mesangial cell, etc.
See more: check the image below, and check the Renal Corpuscle connectome card page.
Cell Differentiation and Lineage:
Kidney cells arise from OSR1+ mesenchymal progenitor cells in the intermediate mesoderm. As a kidney epithelial cell, podocyte arises from cap mesenchyme progenitor cells and requires activation of SIX2, PAX2 and WT1. Nephrogenic mesenchymal cells initially form mesenchymal condensates, and then transform into epithelial cells during the comma-shaped body stage to the S-shaped body stage. Refs: PMC4163204 and PMC1853414.
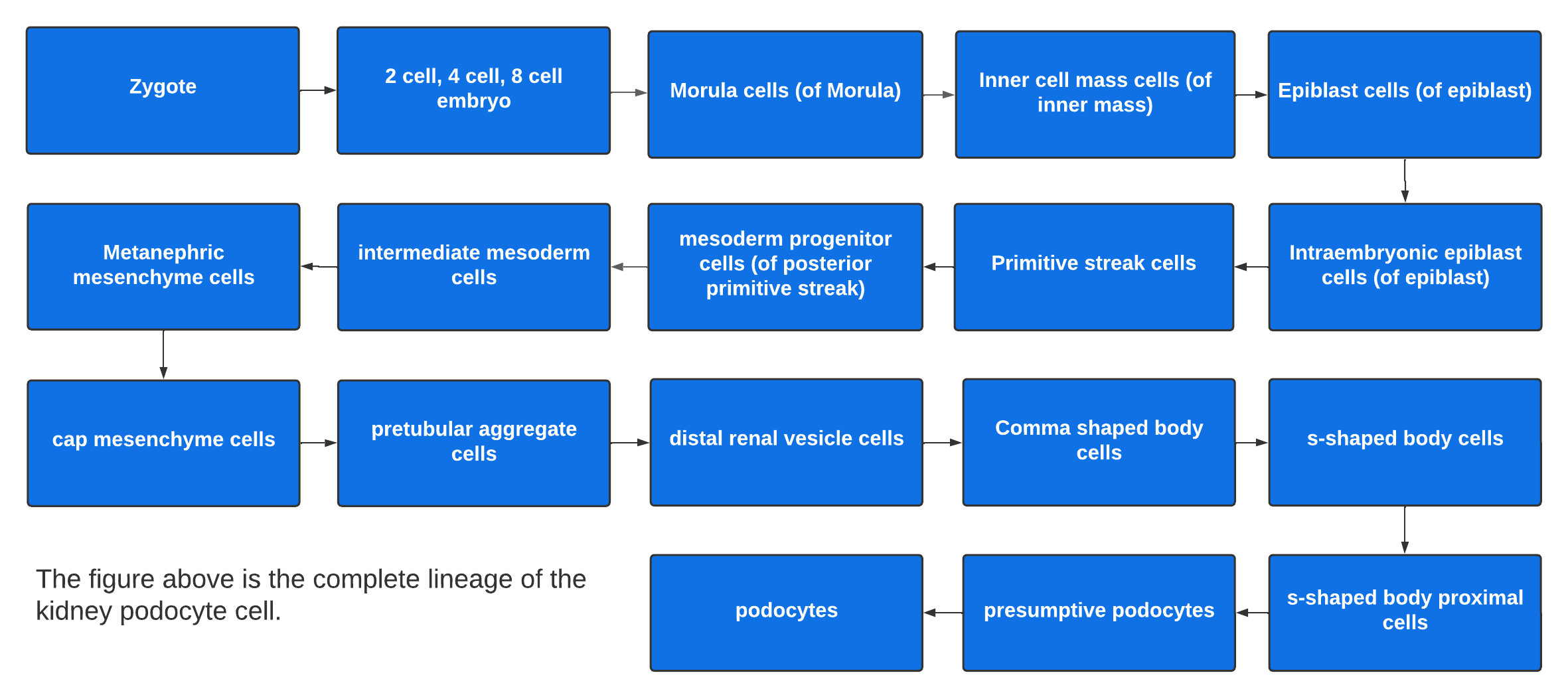
Starting from zygote, the podocyte cell lineage undergoes many steps as shown in the folllowing figure:
Above is a graphic (prepared by: Fatima Oudeif and Oliver He) showing of the complete lineage of podocyte starting from zygote. Many molecules and cell differentiation regulation processes are required for the podocyte formation as illustrate in a more detailed podocyte cell lineage figure (prepared by Fatima Oudeif and Andrew Lloyd). Refs: LifeMap, and PMC9338909.
Cell Type Evolution Among Organisms:
Many invertebrate animals have cells analogous or homologous to podocyte, including:
- Worm excretory cell: https://cellcards.org/worm_excretory_cell.php.
- Fly pericardial nephrocyte: https://cellcards.org/fly_pericardial_nephrocyte.php. As seen in Fig. 5 in the PNAS paper Xu et al, 2022, mouse kidney podocytes are aligned with adult Drosophila pericardial nephrocytes. The Fig. 1 in another study by Na et al. 2015 also shows fruit fly adult pericardial nephrocytes are analogous to the podocytes.
Key Gene Ontology Terms associated with Podocyte:
Podocyte-associated GO Cellular Component terms:
- nephrocyte diaphragm (GO_0005917): A specialized cell-cell junction found between nephrocytes of the insect kidney, which is adapted for filtration of hemolymph. The insect nephrocyte is anatomically and functionally similar to the glomerular podocyte of vertebrates.
- podocyte foot (process) (GO_0098846): The podocyte foot processes called pedicels wrap around the capillaries and leave slits between them. Blood is filtered through these slits, each known as a filtration slit, slit diaphragm, or slit pore.
- podocyte primary projection (GO_0003093): A cell projection originating from a renal glomerular podocyte and extending to the renal glomerular podocyte foot.
- slit diaphragm (GO_0036057): A specialized cell-cell junction found between the interdigitating foot processes of the glomerular epithelium (the podocytes) in the vertebrate kidney, which is adapted for facilitating glomerular filtration.
Podocyte-associated GO Biological Process terms:
- glomerulus development (GO_0032835)
- glomerular parietal epithelial cell fate commitment (GO_0072147)
- mesonephric glomerulus development (GO_0061224)
- mesonephric glomerular parietal epithelial cell fate commitment (GO_0061255)
- mesonephric podocyte cell fate commitment (GO_0061258)
- mesonephric podocyte development (GO_0061257)
- mesonephric podocyte differentiation (GO_0061256)
- metanephric glomerulus development (GO_0072224)
- metanephric glomerular parietal epithelial cell fate commitment (GO_0072247)
- metanephric podocyte cell fate commitment (GO_0072250)
- metanephric podocyte development (GO_0072249)
- metanephric podocyte differentiation (GO_0072248)
- negative regulation of podocyte apoptotic process (GO_1904634)
- podocyte apoptotic process (GO_1903210)
- podocyte cell fate commitment (GO_0072149)
- podocyte cell migration (GO_0090521)
- podocyte development (GO_0072015)
- podocyte differentiation (GO_0072112)
- positive regulation of metanephric podocyte development (GO_2000478)
- positive regulation of podocyte apoptotic process (GO_1904635)
- regulation of glomerular filtration (GO_0003093)
- regulation of podocyte apoptotic process (GO_1904633)
- slit diaphragm assembly (GO_0036060)
Cell Biomarkers:
Podocyte-related biomarkers (Ref: HuBMAP ASCT-B Tables):
- NPHS1 (nephrin): OGG_3000004868. PR_000011365. HGNC: 7908. GeneCards: NPHS1. References: PMC6597610 , PMC7213795, PMC6597610
- NPHS2 (podocin): OGG_3000007827. PR_000011366. HGNC: 13394. GeneCards: NPHS2. References: PMC6597610, PMC7213795.
- PODXL (podocalyxin): OGG_3000005420. PR_000012955. HGNC:9171. GeneCards: PODXL. References: PMC6597610, PMC7213795, PMC6597610.
- PTPRQ (Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor Type Q): OGG_3000374462. PR_000013477. HGNC: 9679. GeneCards: PTPRQ.
Check more: Podocyte-LM page that includes more literature mined podocyte biomarker information.
Ligands and Receptors expressed in Podocytes:
As an component of the mammalian kidney filtration apparatus, podocytes process a series of intercellular signals. At the interface of blood and urine, podocyte membranes comprise three distinct signalling platforms: the sole plate (baso-lateral membrane attached to the glomerular basement membrane), slit diaphragm (cell-to-cell junction formed between adjacent podocytes), and apical membrane that extends into the urine space. See Figure 1 in PMC4109315.
Podocytes express many signal transduction receptors, including receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), and nuclear receptors. Podocytes also expresses integrins, which mediate cell matrix adhesion as well as outside-in signalling. Ref: PMC4109315.
Activation of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) on cultured human podocytes induces CD80 expression and phenotypic change via an NF-?B-dependent mechanism. The results provide a mechanism by which viral infections may cause proteinuria. Ref: PMID: 21617192.
Neighborhood Cell Types of Podocyte:
The neighborhood cell types of podocyte are described in detail in the Renal Corpuscle Cell Connectome page.
Literature mined Podocyte-related Gene-gene Interactions:
Please find literature mined results using Ignet:
Gene Expression Profiles:
Selected podocyte-associated gene expression studies:
- GSE1545: Human podocyte differentiation. Organism: human.
- E-GEOD-39441: Molecular fingerprint of the podocyte reveals novel gene regulatory networks. Organism: mouse.
- See more: GEO search, and ArrayExpress Search.
Pathways and Functional Maps:
Podocyte-associated pathways and functional maps:
- Nephrin family interactions: Reactome: R-HSA-373753.
- See more: Reactome search.
Images:
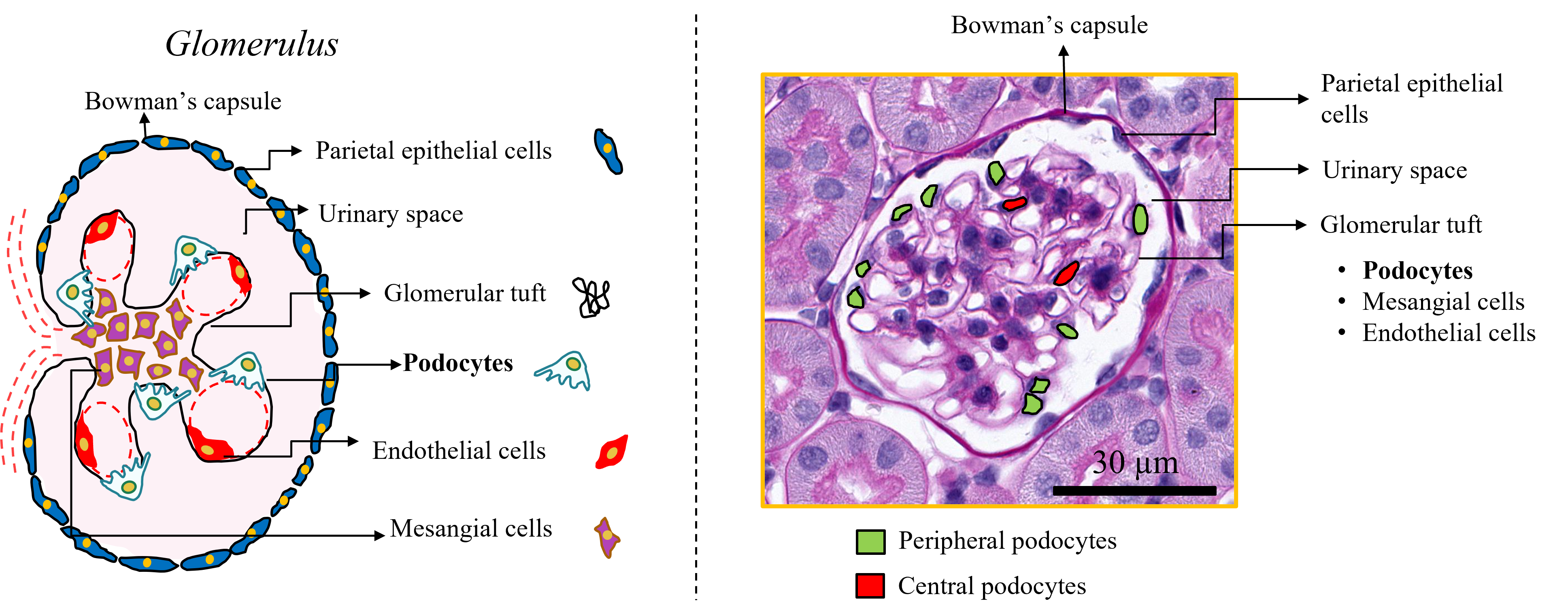
Below are two images showing the podocytes inside the glomerulus:
Left: The glomerulus structure that contains podocytes and other cells. Right: peripheral and podocytes highlighted. Copyright: Pinaki Sarder.
Note: The Sarder Lab Slide Analyzer and PodoSighter can be used to support podocyte image study.
Cell Line Cells:
The following cell lines are available:
- Human podocyte cell line cells:
- CIHP-1: Conditionally Immortalized Human Podocytes-1. Synonymes: AB8/13; AB 8/13; hiPOD. CLO_0037390. See also: CVCL_W186.
- hAKPC-P: human Amniotic-fluid Kidney Progenitor Cells-Podocytes. CLO_0037391. See also: CVCL_YP01.
- HGVEC.SV1: Human Glomerular Visceral Epithelial Cells.SV40 transformed 1. CLO_0037392. See also: CVCL_WW27.
- HGVEC.SV1A4: Human Glomerular Visceral Epithelial Cells.SV40 transformed 1 clone A4. Synonymes: HGVEC.SV1 clone A4; HGVEC. CLO_0037393. See also: CVCL_WW28.
- HUPEC 001 G0/G0. Disease: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. CLO_0037394. See also: CVCL_B0C8.
- HUPEC 002 FSGS G0/G0. Disease: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. CLO_0037395. See also: CVCL_B0D0.
- HUPEC 003 FSGS G0/G0. Disease: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. CLO_0037396. See also: CVCL_B0C9.
- HUPEC 005 FSGS G1/G2. Disease: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. CLO_003739. See also: CVCL_B0CA.
- STBCi028-A. Synonymes: SFC018-03-01; SFC018 clone 03-01. CLO_0037398. See also: CVCL_RB91.
- STBCi321-A: Induced pluripotent stem cell. Synonymes: SFC-AD2-01; SB-AD2c1; AD2c1; SBAD02-01; SBAD2-01; SB AD2.1; SBAD2 clone 1. CLO_0037399. See also: CVCL_ZX54.
- STBCi322-A: Induced pluripotent stem cell. Synonymes: SFC-AD3-01; SB-AD3c1; AD3c1; SBAD03-01; SBAD3-01; SBAD3-1; SB AD3.1; SBAD3 clone 1. CLO_0037420. See also: CVCL_ZX55.
- Mouse podocyte cell line cells:
- E11 [Mouse]: CLO_0037384. CVCL_5737.
- MPC-1: Mouse Podocyte Clone-1. Synonymes: MPC1. CLO_0037385. See also: CVCL_AS86.
- MPC-5: Mouse Podocyte Clone-5. Synonymes: MPC5. CLO_0037386.See also: CVCL_AS87.
- MPC-8: Mouse Podocyte Clone-8. Synonymes: MPC8. CLO_0037387. See also: CVCL_AS88.
- SVI: derirved from adult mouse. CLO_0037388. See also: CVCL_5943.
- Rat podocyte cell line cells:
- 2DNA1D7: Conditionally immortalized rat podocyte cell. CLO_0037389. See also: CVCL_XF89.
Clinical Significance:
Many "abnormal podocyte cell morphology" (HP_0031265) phenotypes exist:
- Podocyte foot process effacement (HP_0031266)
- Podocyte hypertrophy (HP_0020133)
- Visceral epithelial cell detachment (HP_0033237)
- Podocyte microvillous transformation (HP_0033238)
- Podocyte myelin figures (HP_0033265)
- Glomerular pseudocrescent (HP_0033266)
- Binucleated visceral epithelial cells (HP_0033296)
- Multinucleated visceral epithelial cells (HP_0033297)
- Visceral epithelial cell hyperplasia (HP_0033314)
- Visceral epithelial hyaline droplets (HP_0033315)
- Podocyte infolding (HP_0033483)
- Podocyte cytoskeletal condensation (HP_0033492)
Podocyte-related diseases also exist:
- lipoid nephrosis (MONDO_0006835)
References:
- Wiki: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Podocyte.
- Gene Ontology for podocyte: http://amigo.geneontology.org/amigo/search/ontology?q=podocyte.
- Ontobee search for podocyte: https://ontobee.org/search?ontology=&keywords=podocyte&submit=Search+terms.
- MGI search for podocyte: Podocyte-related mouse informatics.
- Govind D, Becker JU, Miecznikowski J, Rosenberg AZ, Dang J, Tharaux PL, Yacoub R, Thaiss F, Hoyer PF, Manthey D, Lutnick B, Worral AM, Mohammad I, Walavalkar V, Tomaszewski JE, Jen K, Sarder P. PodoSighter: A cloud-based tool for label-free podocyte detection in kidney whole-slide images. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. 32(11):2795-2813. PMID: 34479966.
Note: This is a manually generated website. Lessons learned will be used for automatic cell card content generation. Feedback is welcome. Thanks!